Understanding User Intent Through AI Agent & Bot Traffic
Data Analysis
A growing blind spot is emerging in website analytics: the user intent behind AI assistant traffic.
Every day, AI assistants like ChatGPT, Claude, and Perplexity hit your docs and product pages on behalf of real users asking questions like “How do I integrate [product X]?” or “Is [tool Y] better than [competitor Z] for my use case?” But by the time this traffic reaches your analytics, all that intent has been stripped away. It’s either lumped into generic “bot” categories, aggressively filtered out, or logged with zero context about the underlying question.
The problem isn't simply about logging, it's about context loss. You’re not just missing pageviews, you’re missing the questions behind them. Those “invisible visits” could tell you which features are blocking adoption, which competitors you’re compared against, which pricing pages trigger doubt, and which integrations drive the most qualified demand. Instead, that valuable information vanishes.
By applying an LLM-based framework to analyze AI assistant sessions, we show that this traffic isn’t homogeneous at all. It can be segmented into concrete, high-value intents and turned into a new source of customer intelligence.
Our pilot analysis of TradeVision.io, an options trading platform, uncovered two critical insights:
- First, 47% of AI assistant sessions concentrated on options trading education, pinpointing which topics AI systems most strongly associate with the brand.
- Second, end-users and decision-makers demonstrate opposite behaviors (94% learning vs. 60% comparison), revealing that AI discoverability requires bifurcated content strategies: educational content for awareness, comparison content for conversion, rather than blended approaches that serve neither audience well.
This article outlines how to recover that lost context and turn AI bot logs from trash into a strategic asset for acquisition, content, and product decisions.
1. The Framework in Brief
The Core Innovation: Moving Beyond Traditional Analytics
Most teams try to understand user behavior with URL rules, regex, or embedding-based clustering. The problem: these methods are descriptive, not interpretive. They group hits that look similar on the surface, but they can't reconstruct the story behind a session.
Our approach uses LLMs as reasoning engines to interpret full user journeys rather than isolated pageviews. Instead of pre-defined taxonomies, we let the model dynamically infer who is behind each query and what they're trying to do. This moves us from "this session visited /pricing and /docs" to "this is a developer evaluating integration feasibility based on API limits, then checking whether the pricing fits their use case."
How It Works: The 4-Stage Process
The framework treats every AI bot visit as a breadcrumb trail, reconstructing them into coherent sessions to decode the human intent behind the prompt.
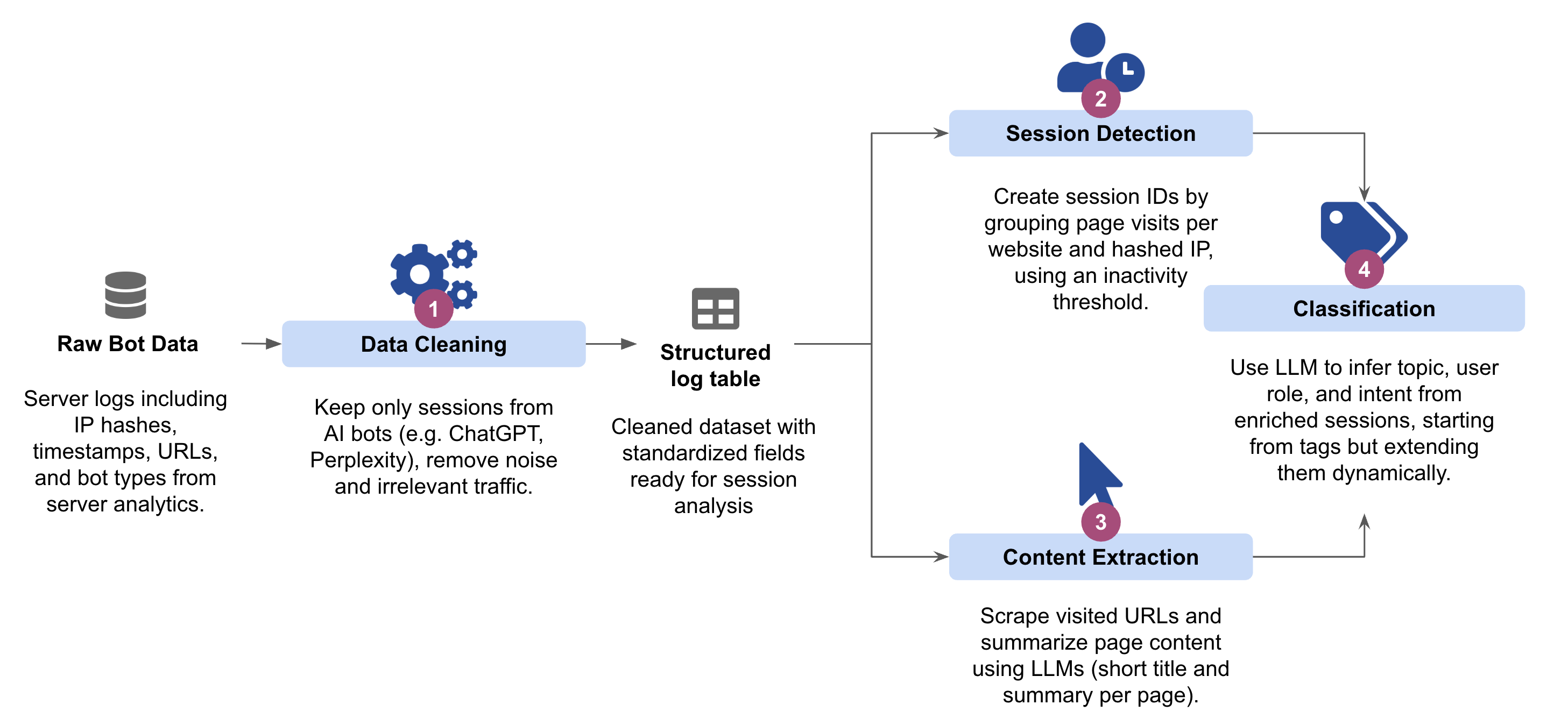
Stage 1: Separating Signal from Noise
Raw server logs are filtered to keep only AI assistants acting on real user queries, removing noise from SEO crawlers, uptime monitors, spam bots, and internal automation.
Stage 2: Reconstructing User Journeys
Individual hits are grouped by IP address and temporal proximity to transform disconnected URLs into coherent browsing narratives. A natural break in activity (e.g., a 5-minute gap) signals the start of a new session.
Stage 3: Semantic Enrichment
The system scrapes every unique page visited and uses a lightweight LLM to generate semantic titles and summaries, translating cryptic URLs (e.g., /docs/v2/auth) into human-readable concepts.
Stage 4: Inferring User Intent A reasoning LLM analyzes the full enriched journey to answer three core questions, assigning a confidence score to each classification:
- Topic: What is the precise subject? (e.g., "Payment Integration Errors").
- Role: Who is the user? (e.g., Developer vs. Decision-Maker).
- Goal: What are they trying to do? (e.g., Evaluation vs. Active Implementation).
This final stage converts raw data into dynamic, quantified insights that evolve automatically as new content and user behaviors emerge.
2. Case Study: What the Data Actually Reveals
Let’s see what happens when the framework is applied in practice. For this analysis, server logs were collected from three pilot websites over a 24-hour period from Tradevision.com and filtered to keep only ChatGPT-User bot traffic. This traffic is user-initiated: it is triggered when real users ask ChatGPT questions, which makes it a reliable proxy for genuine interest and intent.
Anatomy of an AI-Mediated Session
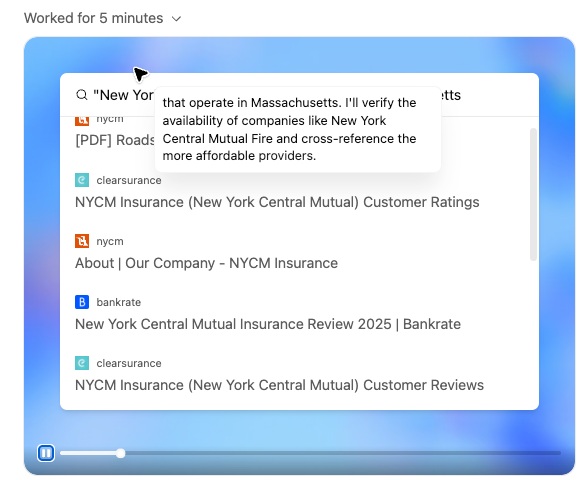
Before examining aggregate patterns across thousands of sessions, let's trace a single journey to understand what session reconstruction and LLM-based classification reveals and why it matters.
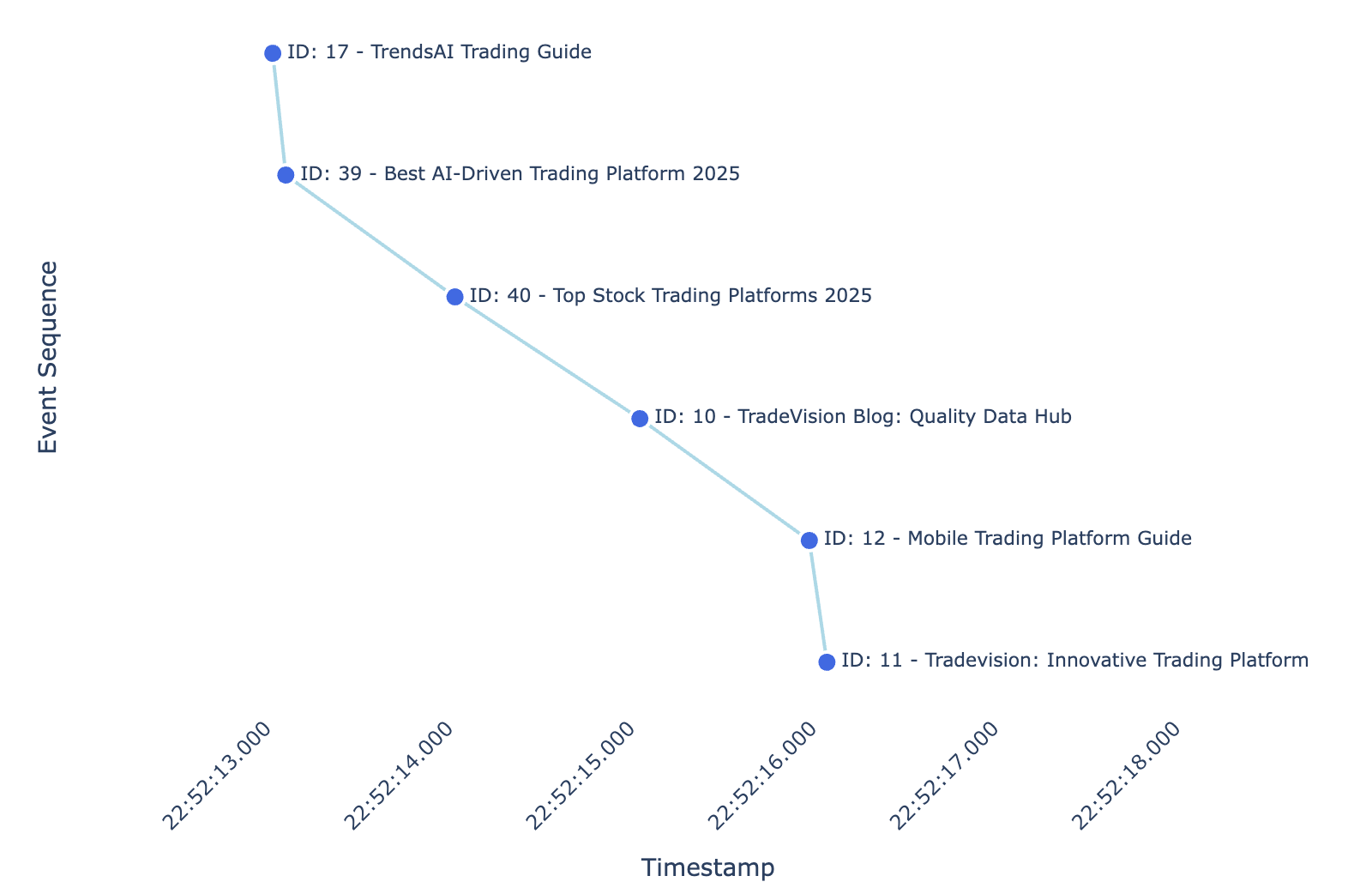
The framework's LLM classifier analyzed this sequence and produced:
- Topic: Trading platform review
- User Role:
decision-maker(confidence: 90/100) - Intent Type:
comparison(confidence: 92/100) - Reasoning: The session comprises multiple TradeVision blog pages focused on comparing and evaluating trading platforms (AI-driven tools, 2025 platform rankings, mobile vs desktop, and platform reviews). This indicates a decision-making, comparison-oriented intent rather than learning or implementation.
This session likely reflects a user asking something like “What’s the best AI trading platform for mobile in 2025?” The assistant gathered comparative information step by step, moving from general guidance to specific recommendations to product details.
The next sections scale this analysis across thousands of sessions to reveal broader patterns in user segmentation, content performance, and optimization priorities.
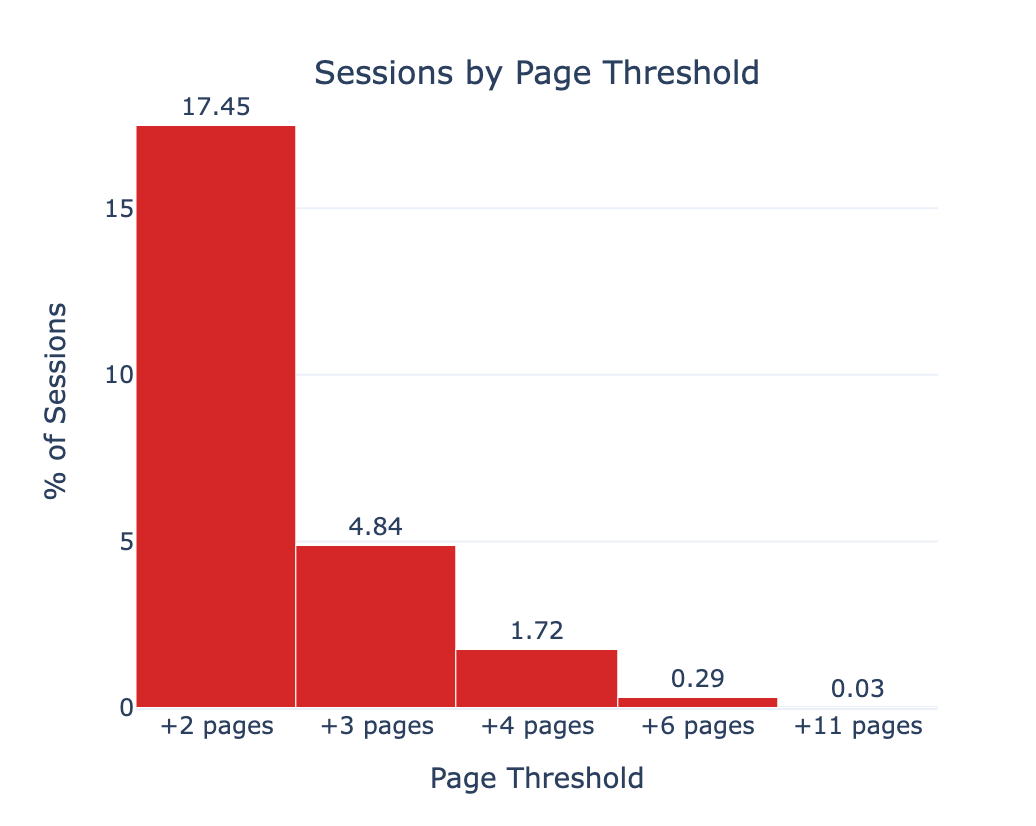
Session Duration and Engagement Patterns
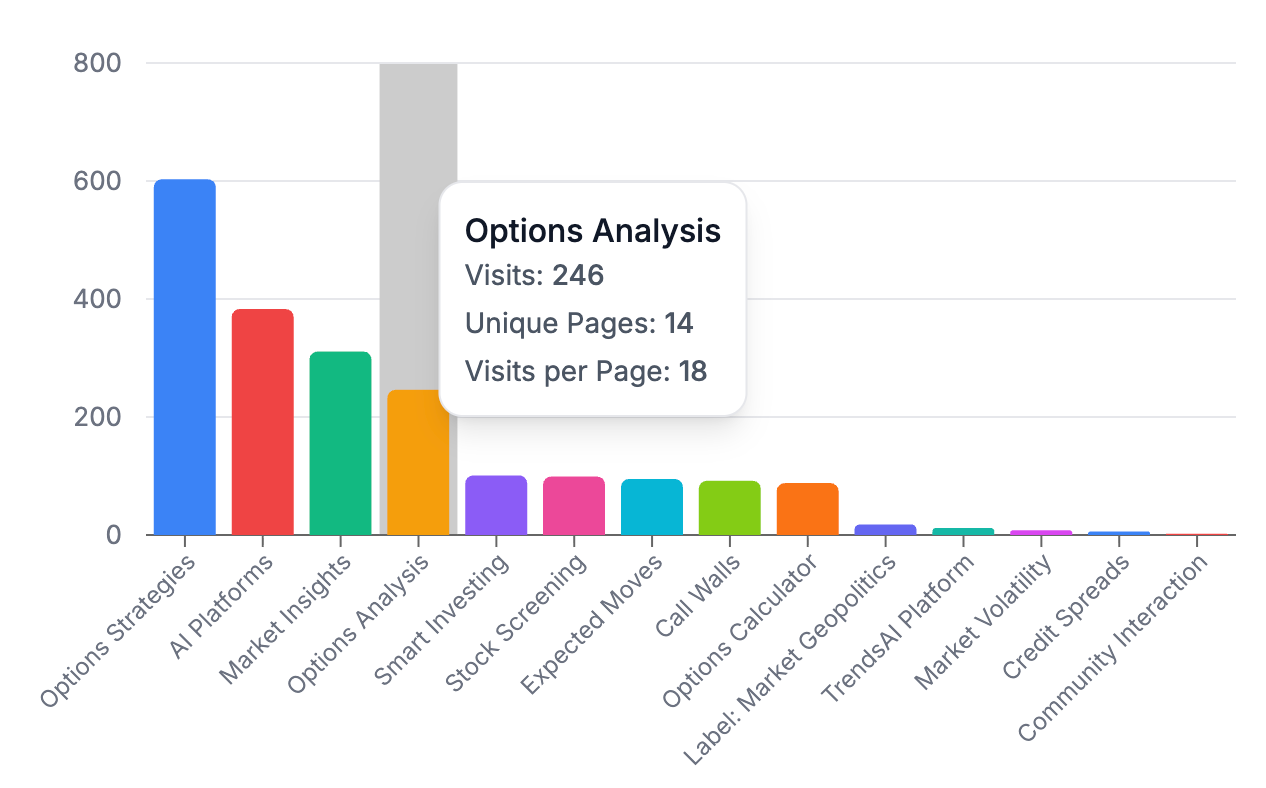
The analysis revealed that AI-mediated sessions are short and focused. Most sessions last only a few seconds and contain only one or two unique pages. However, a small fraction exceed three as shown in the graph below. Although rare, these longer chains are interesting to examine as they often map to higher-intent behaviors such as comparisons, troubleshooting, or multi-step reasoning.
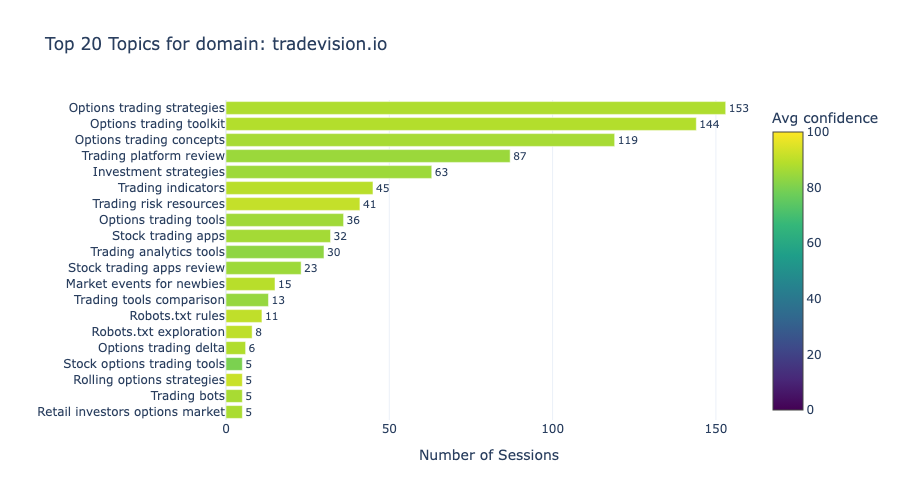
Topic Distribution: Identifying Content Opportunities
The traffic data reveals two dominant themes: strong demand for options trading education and consistent interest in platform comparison content. Understanding these patterns helps identify where content investment delivers the highest return for tradevision.io in AI search visibility.
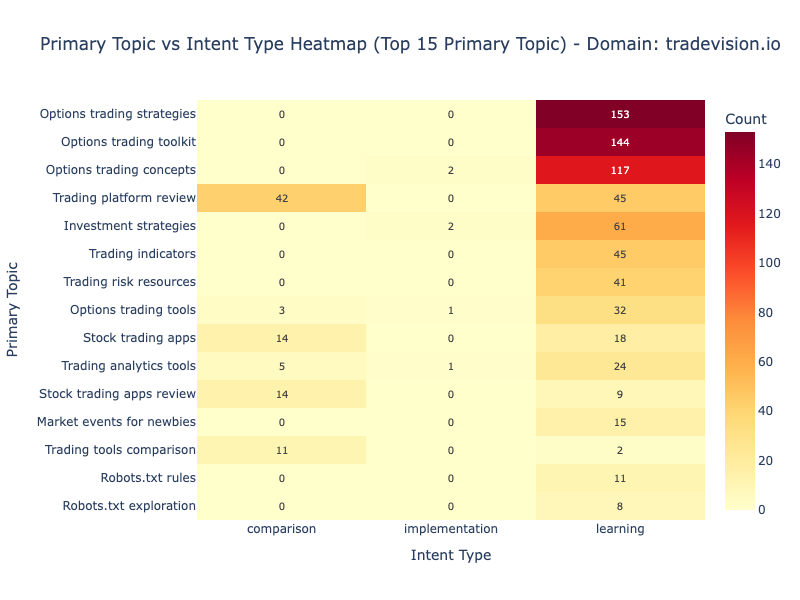
Figure 4 shows that options trading content captures over 400 sessions across three related topics: "Options trading strategies" (153), "Options trading toolkit" (144), and "Options trading concepts" (119). Together, these three topics account for 47% of all sessions, out of a total of 873.
The topic-intent relationship displayed in below shows distinct patterns. Options content attracts pure learning intent while "Trading platform review" shows balanced distribution, indicating the content successfully serves both discovery and evaluation stages.

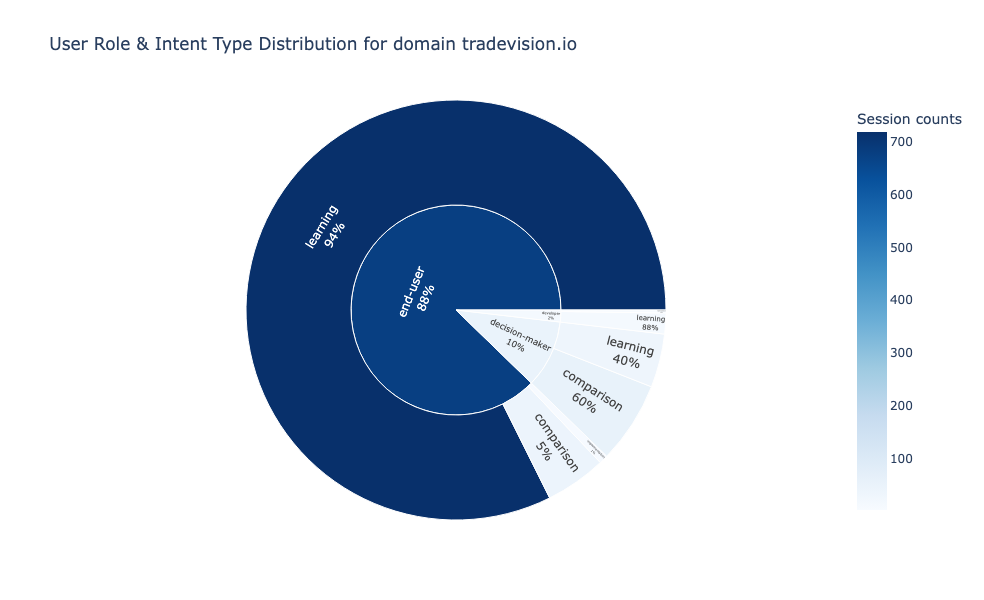
User Segmentation: Understanding User Roles, Intent, and Behavioral Patterns
The findings become even stronger when we analyze the user-level segmentation.
In the chart beelow, we can see that end-users represent the majority of traffic and demonstrate 93.9% learning intent with minimal comparison (5.4%). Decision-makers show the inverse pattern: 60.4% comparison intent with secondary learning (39.6%).
These fundamentally different browsing behaviors reflect different stages in the consideration journey, end-users building knowledge, decision-makers actively evaluating alternatives.
3. Why This Matters: Strategic Implications
The Zero-Click Blind Spot
For Tradevision, AI assistants account for 17% of all sessions to content about options trading strategies . Traditional analytics, however, register zero visits, zero engagement, zero value. And yet, real users received answers, while AI systems began associating TradeVision with expertise in options trading.
This is the core challenge: content is delivering business value without activating conventional success metrics. Companies focused only on direct traffic are measuring a shrinking slice of how users actually discover, evaluate, and understand their products. This framework surfaces that hidden demand.
Early Signal Detection as Competitive Edge
AI assistants capture user intent long before a prospect commits to visiting a website, trying a product, or contacting support.
Consider the case of TradeVision. By analyzing AI search behavior, they detected a surge of decision-makers on platform comparison pages. The catch? There was near-zero intent to actually implement the software. Traditional funnel analysis would simply see this as "bounced traffic," but AI signals revealed the truth: a hidden onboarding gap.
This kind of signal allows for a predictive strategy:
- Fix friction before it escalates into support tickets.
- Expand content before feature requests pile up.
- Claim ownership of topics before competitors even notice the trend.
The Compound Effect: Most importantly, this first-mover advantage compounds over time. When AI assistants consistently cite TradeVision for options trading, they build deep mental associations. Competitors entering the market later face a steeper challenge: they must not only match the product but also unseat an established algorithmic bias in your favor.
AI Discoverability: The New Game
While traditional SEO focuses on visibility on a search engine results page, AI discoverability focuses on retrieval and citation. The goal is to be the primary source used by an assistant to generate an answer, often without the user ever visiting a website.
This shift demands that we prioritize structure over keywords.
TradeVision exemplifies this success. Their content performs well not due to backlink volume, but because it is architected for synthesis as it provides self-contained, comprehensive answers. Conversely, content strategies that fragment information across multiple pages perform poorly in AI-mediated discovery.
Our framework allows you to audit your digital footprint, identifying which assets successfully serve this new discovery layer and which are invisible to the algorithms that matter most.
What’s Next?
Businesses are standing at a crossroads: they can continue to filter out AI bot traffic as "measurement noise," or they can recognize it for what it truly is, the earliest signal of user intent from the next generation of customers who leverage AI tools.
Using the framework we've provided savvy marketers can go beyond just measuring this shift and learn to capitalize on it.
Ready to unlock growth insights from your own server log files? GPTrends Agent Analytics is a free product to help optimize AI search with your own website data.
Sign up for a free account then review which now / low code integration options work best for your website.